Graph
A Graph consists of a finite set of vertices (or nodes) and set of Edges which connect a pair of nodes.
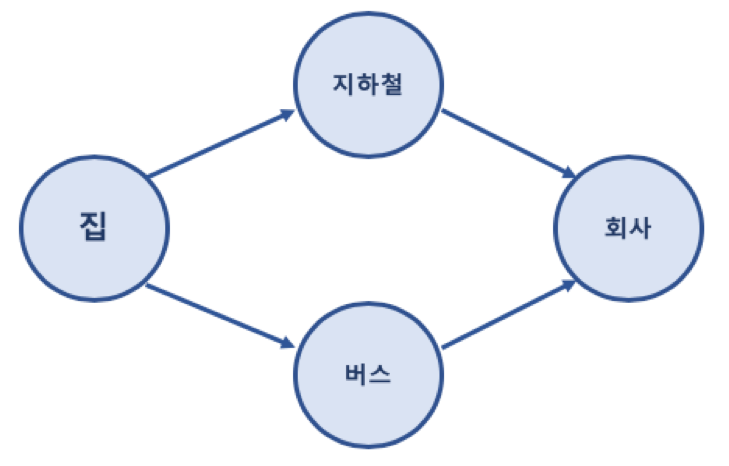
Terms
Mathematical graphs can be represented in data structure. We can represent a graph using an array of vertices and a two-dimensional array of edges. Before we proceed further, let's familiarize ourselves with some important terms
Vertex ( Node )
: Each node of the graph is represented as a vertex. In the following example, the labeled circle represents vertices. Thus, A to G are vertices. We can represent them using an array as shown in the following image. Here A can be identified by index 0. B can be identified using index 1 and so on.
Edge
: represents a path between two vertices or a line between two vertices. In the following example, the lines from A to B, B to C, and so on represents edges. We can use a two-dimensional array to represent an array as shown in the following image. Here AB can be represented as 1 at row 0, column 1, BC as 1 at row 1, column 2 and so on, keeping other combinations as 0.
Adjacency
: Two node or vertices are adjacent if they are connected to each other through an edge. In the following example, B is adjacent to A, C is adjacent to B, and so on.
Path
: Path represents a sequence of edges between the two vertices. In the following example, ABCD represents a path from A to D.

Reference terms
아직까지 필요해본적이 없음
정점의 차수 ( Degree ): 무방향 그래프에서 하나의 정점에 인접한 정점의 수
진입 차수 ( In-Degree ): 방향 그래프에서 외부에서 오는 간선의 수
진출 차수 ( Out-Degree ): 방향 그래프에서 외부로 향하는 간선의 수
경로 길이 ( Path Length ): 경로를 구성하기 위해 사용된 간선의 수
단순 경로 ( Simple Path ): 처음 정점과 끝 정점을 제외하고 중복된 정점이 없는 경로
사이클 ( Cycle ): 단순 경로의 시작 정점과 종료 정점이 동일한 경우
Implementation
Last updated